In 2010 there were several changes in the structure of earnings
The median of gross monthly earnings of full-time employees was 16% lower than the average. According to the last survey which was conducted in 2008, the median was 14% lower than the average. The difference of the median and the average shows that over a half of employees earn less than the average.
In 2010, the gross monthly earnings of a full-time employee were 320 euros in the 1st decile and 1,418 euros in the 9th decile. Thus the 9th decile was 4.4 times higher than the 1st decile. Since 2005, the proportion between the 9th and 1st decile has not changed significantly. The relation between the highest and lowest deciles shows the difference of earnings between employees earning low and high earnings.
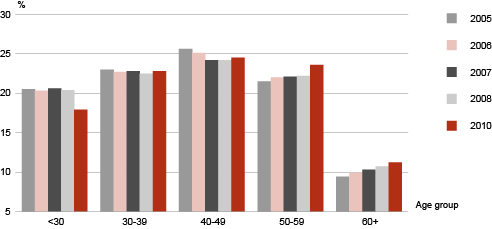
In October 2010, there were 484,000 employees; their number was the biggest in October 2007 (583,500). After the crisis on the labour market in 2009 the structure of employees also changed. The share of male employees in the total number of employees decreased from 47% in 2008 to 45% in 2010. At the same time the share of employees fell 2.5 percentage points among the employees aged less than 30 and rose 1.4 percentage points among the employees aged 50–59.
Employees by age group, 2005–2010 (year = 100)
Statistics Estonia conducts the survey “Structure of Earnings” since 2005 based on the international methodology. The survey is conducted for October. Since 2010, the survey is conducted every four years. In 2010, the sample included 10,872 enterprises, institutions, non-profit organisations and 122,000 employees. It is a thorough earnings’ survey, which provides the consumers with more detailed data compared to the quarterly wages statistics. The data of the survey reflect the number of employees, structure and earnings by occupation, economic activity, age, the kind of contract, full- and part-time employees and education.
The published average gross earnings do not include irregular bonuses and premiums.
Deciles divide employees into ten equal groups. The first decile shows the sum of earnings, of which 10% of employees receive smaller earnings and 90% bigger earnings. The fifth decile serves as a median at the same time, of which half of the employees get bigger and half smaller earnings.